Select SQL Wizard
SQL Wizard
SQL statements can be easily created with the wizard.
Starting Select SQL Wizard
To start SQL Wizard, click SQL Wizard in the properties dialog in Execute Select SQL in the database connector.
Screen elements of Select SQL Wizard
Basic settings screen
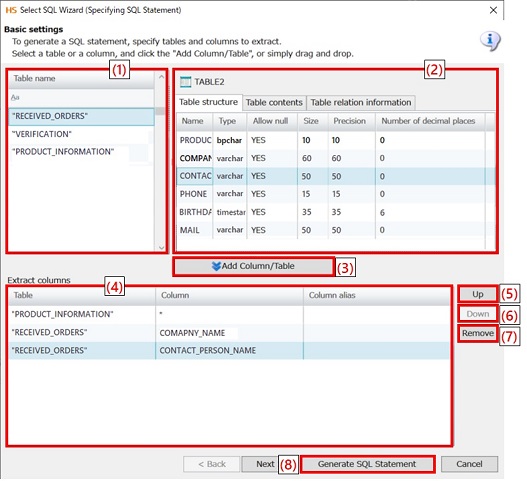
|
Numbering in the figure |
Name |
Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
|
(1) |
Table list view |
Displays a list of tables. |
|
|
(2) |
Table information pane |
Displays the information on the selected table. |
|
|
(3) |
Add Column/Table |
Adds the column selected in the Table structure tab in the table information pane to the extraction column editor. |
|
|
(4) |
Extraction column editor |
Set the writing order of the read columns and an alias (the name of the extraction result column). |
|
|
(5) |
Up |
Moves the selected column up. |
|
|
(6) |
Down |
Moves the selected column down. |
|
|
(7) |
Remove |
Deletes the selected column. |
|
|
(8) |
Generate SQL Statement |
Automatically generates a SQL statement based on the settings. |
|
Join conditions settings screen
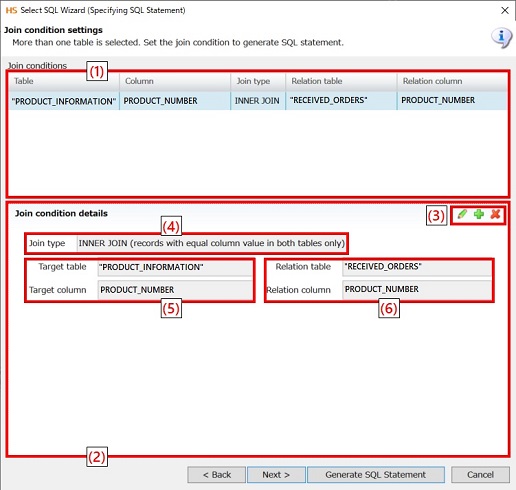
|
Numbering in the figure |
Name |
Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
|
(1) |
Join condition list view |
Displays a list of join conditions between read tables. |
SQL statements are generated in the listed order. |
|
(2) |
Join condition editor |
Configure join conditions between read tables. |
|
|
(3) |
Edit of join conditions |
Add, edit and delete join conditions. |
|
|
(4) |
Join type |
Configure a join type.
|
|
|
(5) |
Target table, Target column |
Set a name for the table and the column to be joined. |
|
|
(6) |
Relation table, Relation column |
Set a name for the table and the column to be joined. |
|
Condition and Sorting settings screen (Condition)
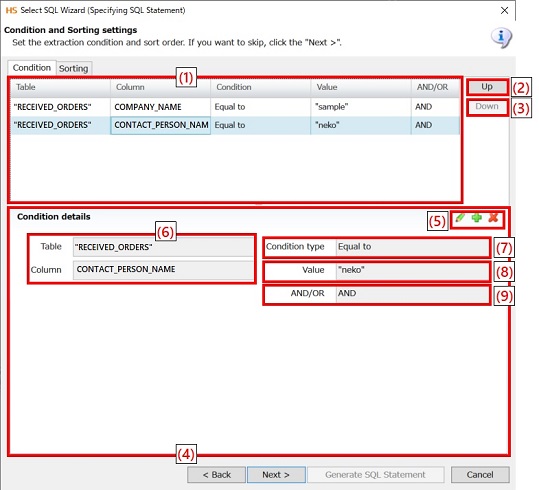
|
Numbering in the figure |
Name |
Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
|
(1) |
Condition and sorting settings |
Displays a list of extraction conditions for a read table. |
SQL statements are generated in the listed order. |
|
(2) |
Up |
Moves an extraction condition up. |
|
|
(3) |
Down |
Moves an extraction condition down. |
|
|
(4) |
Extraction condition editor |
Configure extraction conditions for a read table. |
The extraction conditions are displayed in the extraction condition list view. |
|
(5) |
Edit of extraction conditions |
Add, edit and delete extraction conditions. |
|
|
(6) |
Table, Column |
Set the names for the table and the column for which to specify extraction conditions. |
|
|
(7) |
Condition type |
Configure the type of extraction conditions.
|
|
|
(8) |
Value |
Specify conditions for a read column. |
|
|
(9) |
AND/OR |
Specify a logic operator for multiple conditions.
|
|
Condition and Sorting settings screen (Sorting)
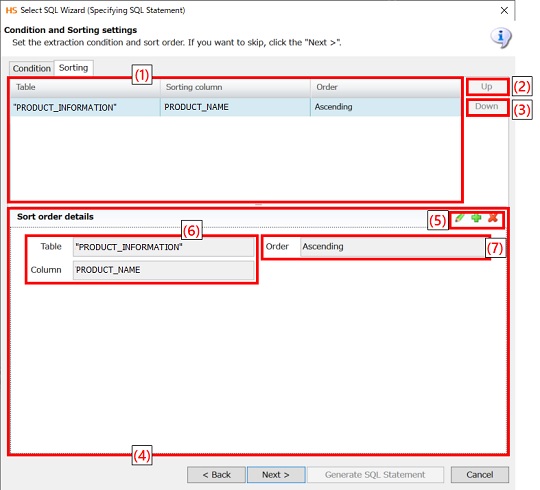
|
Numbering in the figure |
Name |
Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
|
(1) |
Sort conditions list view |
Displays a list of sort conditions for a read table. |
SQL statements are generated in the listed order. |
|
(2) |
Up |
Moves a sort condition up. |
|
|
(3) |
Down |
Moves a sort condition down. |
|
|
(4) |
Sort condition editor |
Configure sort conditions for a read table. |
The sort conditions are displayed in the sort condition list view. |
|
(5) |
Edit of sort conditions |
Add, edit and delete sort conditions. |
|
|
(6) |
Table, Column |
Set the name for the table and the column for which to specify sort conditions. |
|
|
(7) |
Order |
Configure the sort order of a read column.
|
|
Generated SQL statement and execution test screen
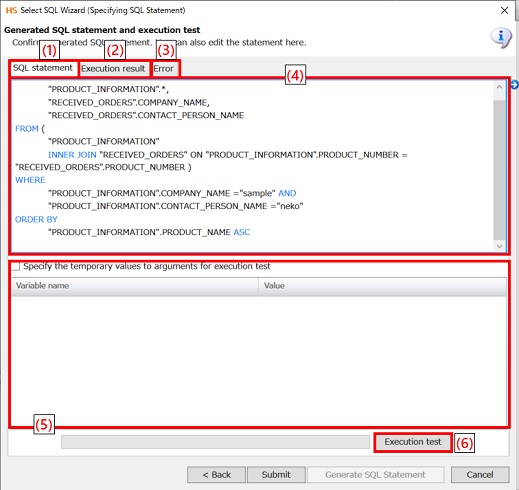
|
Numbering in the figure |
Name |
Description |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
|
(1) |
SQL statement tab |
Displays an automatically generated SQL statement. |
|
|
(2) |
Execution result tab |
Displays the result of test execution. |
|
|
(3) |
Error tab |
Displays errors if errors occur during test execution. |
|
|
(4) |
SQL statement editor |
You can edit an automatically generated SQL statement. You can also write SQL functions which can't be generated in SQL Wizard. |
Note
If a SQL statement is edited manually, it can't be re-edited in the wizard. |
|
(5) |
Setting of formal parameters |
If a script variable is used in an extraction condition, you can replace the script value with the value that is set in Value and execute a test of the SQL statement. This is enabled if Specify the temporary values to arguments for execution test is selected. |
Note
It isn't possible to specify a formal parameter to an environmental variable or a SQL parameter. |
|
(6) |
Execution test |
Executes a SQL statement. |
|
Generating a SQL statement
To generate a SQL statement, follow the steps below.
-
Select the table you want to read from the table list view and click Add Column/Table. (To specify a read column, select the column in the table information pane.)
-
To specify the definition order of the read columns and an alias, configure them with the extraction column editor.
-
To generate a SQL statement with the settings configured so far, click Generate SQL Statement.
= Remarks =-
To join multiple tables, refer to Join multiple tables.
-
If you want to specify a table not as a read table but in the join condition, refer to How to join tables not specified in a read table.
-
To specify conditions for reading, click Next and refer to Extraction condition settings and Setting the sort order.
-
-
A SQL statement generated in the SQL statement editor in the SQL statement tab is displayed.
Click Submit to save the SQL statement and end SQL Wizard.
-
To execute the SQL statement, click Execution test.
= Remarks =If a script variable is specified in the SQL statement, you can enter values for the variable and execute the statement.
-
It is executed with empty characters if no value is entered.
-
Entered values don't affect the script execution.
-
-
The results are shown in the Execution result tab.
-
If an error occurs during test execution, the error is displayed in the Error tab.
-
Click Submit to save the SQL statement and end SQL Wizard.
-
To edit a SQL statement, click SQL Wizard in the properties settings dialog in Execute Select SQL to start SQL Wizard.
NoteWhen a SQL statement created by SQL Wizard has been manually edited, it can't be re-edited in the wizard.
Start the wizard by selecting in the dialog whether to create a new SQL statement or edit a SQL statement that was created in the wizard.
To join multiple tables, follow the steps below.
-
Click Add in the Joint condition settings screen.
-
In the join condition editor, specify the column for the join key in Target table/Target column as well as Relation table/Relation column.
-
Select Join type.
Item Description
Item name
Description
Remarks
INNER JOIN (records with equal column value in both tables only)
For both the right and left tables, records are retrieved only if the column values are identical.
-
The left table indicates a column specified in Target table/Target column.
-
The right table indicates a column specified in Relation table/Relation column.
LEFT OUTER JOIN (all records on the left and records with equal column value on the right)
For the left table, all records are retrieved. For the right table, records are retrieved only if the column values are identical.
RIGHT OUTER JOIN (all records on the right and records with equal column value on the left)
For the right table, all records are retrieved. For the left table, records are retrieved only if the column values are identical.
Example: The "Products" table and the "Sales" table are joined using "Product No." as a key.
Products
Sales
Product No.
Product Name
1
Product A
2
Product B
4
Product D
Product No.
Order amount
1
10
2
30
3
50
-
INNER JOIN (records with equal column value in both tables only)
Results
Product No.
Product Name
Order amount
1
Product A
10
2
Product B
30
-
LEFT OUTER JOIN (all records on the left and records with equal column value on the right)
Results
Product No.
Product Name
Order amount
1
Product A
10
2
Product B
30
4
Product D
-
RIGHT OUTER JOIN (all records on the right and records with equal column value on the left)
Results
Product No.
Product Name
Order amount
1
Product A
10
2
Product B
30
3
50
-
How to join tables not specified in a read table
For Target table/Relation table, the tables added to the extraction column editor in the Basic settings screen are displayed.
In a case you want to specify a table which isn't added in the extraction column editor, you first need to add the table to the extraction column editor and configure join conditions settings. Then go back to the Basic settings screen to delete the table.
Example:
SELECT tableA.* FROM ( tableA INNER JOIN tableB ON tableA.primaryKey = tableB.primaryKey )
To generate a SQL like above, follow the steps below.
-
In the Basic settings screen, add "tableA" and "tableB" to the extraction column editor.
-
Click Next to jump to the Join condition settings screen.
-
Create a join condition between the "tableA" and the "tableB".
-
Click Back to jump to the Basic settings screen, and delete "tableB" from the extraction column editor.
-
Click Generate SQL Statement.
To configure extraction conditions, follow the steps below.
-
In the Condition and Sorting settings screen, select the Condition tab and click Add.
-
In the extraction condition editor, specify the column for the condition in Table/Column.
-
In the extraction condition editor, specify Condition type and Value.
-
If conditions for multiple columns are required, set logic operators (AND/OR).
Select AND or OR from the AND/OR column list.
To set the order for sorting, follow the steps below.
-
In the Condition and Sorting settings screen, select the Sorting tab and click Add.
-
In the sort condition editor, specify the column for the condition in Table/Column.
-
Select the sort order (Ascending or Descending) in Order.
Automatic Addition of Single Quotes
If the column data type is one of the below, single quotes are automatically added to Value that is set in the extraction condition editor.
- CHAR
- NCHAR
- VARCHAR
- NVARCHAR
- VARCHAR2
- NVARCHAR2
- TEXT
- MEDIUMTEXT
- LONGTEXT
Specification limits
-
Tables which include "." in the schema name or the table name on the database can't be used.
-
Test execution may be failed if the data amount is huge.
-
The maximum record count shown in the Execution result tab is 100.
-
SQL statements can be re-edited only if the tables in the SQL statement exist.
Exception messages
None.