Perform the four basic arithmetic operations for the acquired data and output the results
This section describes the processing of calculating the four basic arithmetic operations for the data acquired from the equipment and outputting the result.
This process outputs results such as the following:
- Example
-
-
Add
If the input value (augend) is "21.394" and the input value (addend) is "2," the output value is "23.394".
-
Subtract
If the input value (minuend) is "21.394" and the input value (subtrahend) is "2," the output value is "19.394".
-
Multiply
If the input value (multiplicand) is "21.394" and the input value (multiplier) is "2," the output value is "42.788".
-
Divide
If the input value (dividend) is "21.394" and the input value (divisor) is "2," the output value is "10.697".
-
Description of the processing
The data and numerical constants acquired from the equipment are calculated with the four basic arithmetic operations and the results are output.
A logic for each of the following is available: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. You can place and use one or more logics. In the following example, four logics are placed:
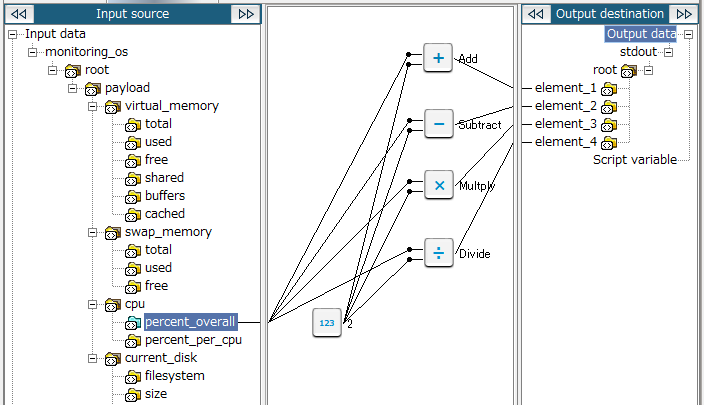
Key features
- Add
-
This logic adds the augend (numerical value of the first input handler) and addend (numerical value of the second input handler) and outputs it.
It can be set from Number > Calculation > Add of the tool palette.
- Subtract
-
This logic subtracts the subtrahend (numerical value of the second input handler) from the minuend (numerical value of the first input handler) and outputs it.
It can be set from Number > Calculation > Subtract of the tool palette.
- Multiply
-
This logic multiplies the multiplicand (numerical value of the first input handler) by the multiplier (numerical value of the second input handler) and outputs it.
It can be set from Number > Calculation > Multiply of the tool palette.
- Divide
-
This logic divides the dividend (numerical value of the first input handler) by the divisor (numerical value of the second input handler) and outputs it.
It can be set from Number > Calculation > Divide of the tool palette.
= Remarks =If the value is not divisible, the output value is a recurring decimal.
Operation procedure
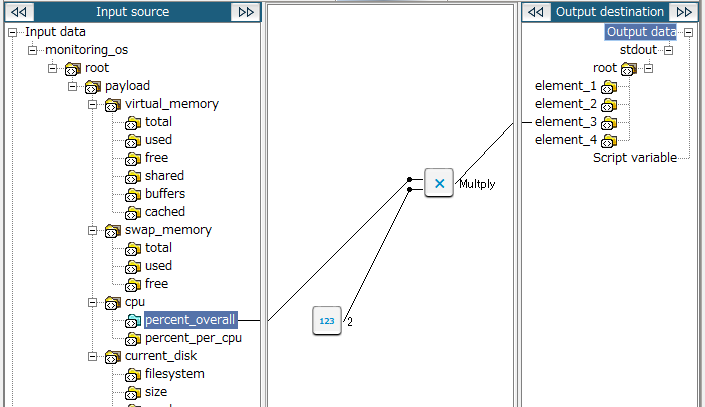
This section describes an example when "Numerical value of the input destination multiplied by 2" is output using the Multiply logic.
1. Create a script.
For information about how to create a script, refer to First Step Guide.
The descriptions in this procedure are based on the following scripts:
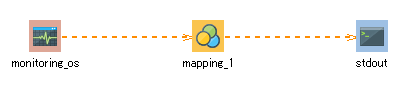
2. On the script canvas, double-click mapping_1.
The Mapper editor is displayed.
3. Drag and drop the following logics from the tool palette onto the Mapper editor:
-
Number > Calculation > Multiply (for multiplying)
-
Number > Basic > Numeric constant (integer) (when the multiplier is an integer value)
The logics are placed on the Mapper editor.
4. Enter the property of the placed logic.
-
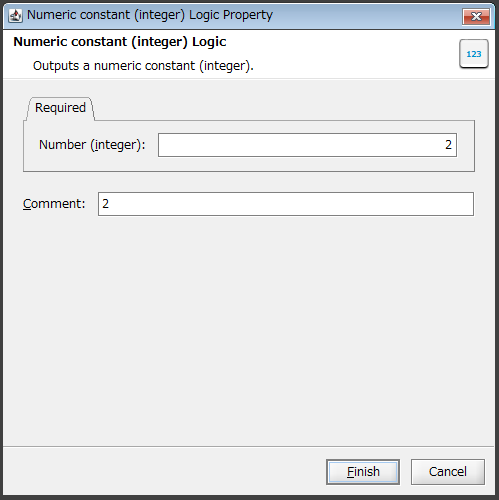
Double-click the Numeric constant (integer) logic.
The Numeric constant (integer) Logic Property dialog box is displayed.
-
Enter a multiplier in Number (integer).
In this example, "2" is entered.
-
If necessary, enter a comment in Comment and click Finish.
-
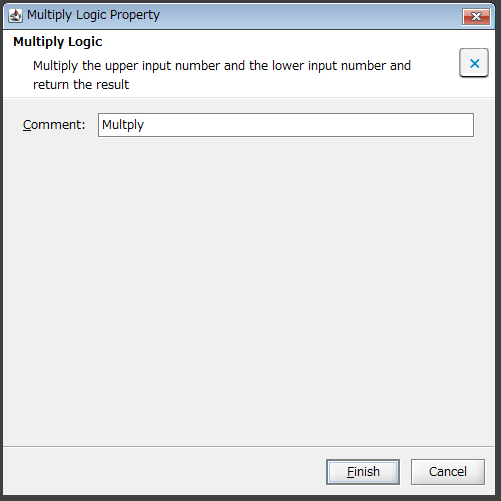
If necessary, double-click the Multiply logic, enter a comment in Comment, and click Finish.
5. Drag and drop the input source node and the Numeric constant (integer) logic onto the Multiply logic (multiplicand on the first input handler and multiplier on the second input handler).
The mapping link to the Multiply logic is displayed.
6. Drag and drop the Multiply logic onto the output destination node (or another logic).
The mapping link to the output destination from the Multiply logic is displayed.
7. Save the script.
For information about how to save a script, refer to First Step Guide.