Fixed-length text files
Fixed-length text files
This section explains about fixed-length text files (hereinafter "fixed-length files").
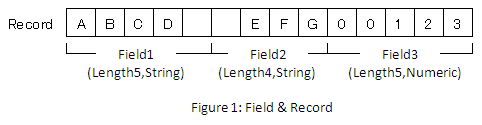
The most basic structural elements of fixed-length files are records. A record represents one line in a text file, and from the start to the end of a line (newline character) is called one record. Each record consists of multiple fields, and each field is separately divided up into its own fixed length. (Figure 1)
You can specify a type (string, number, date, tag) for each field. String, number, and date are used to check the consistency of fields.
A tag is a record identification code. Specify a tag as a string. By specifying a tag, you can correctly handle fixed-length transactions (looping of lines until a string appears in a specific position).
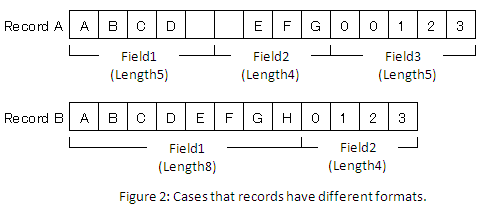
In HULFT Square, all records don't have to be in the same format, and the number and types of fields can vary.
You can also specify the number of times a record appears. Specify this in cases such as when a record definitely appears in three lines. It's also possible to specify no limitations (0 to limitless).
The handling of multiple records as one bunch is called a group (Figure 3). Each record included in the group is organized in the order it appears in the fixed-length file, and the number and types of fields specified for each record must match the fixed-length file exactly.
In the same way as fields for records, in each group the order and number of records that a group consists of may vary.

You can also specify the number of times each group appears. It's also possible to specify no limitations (0 to limitless).