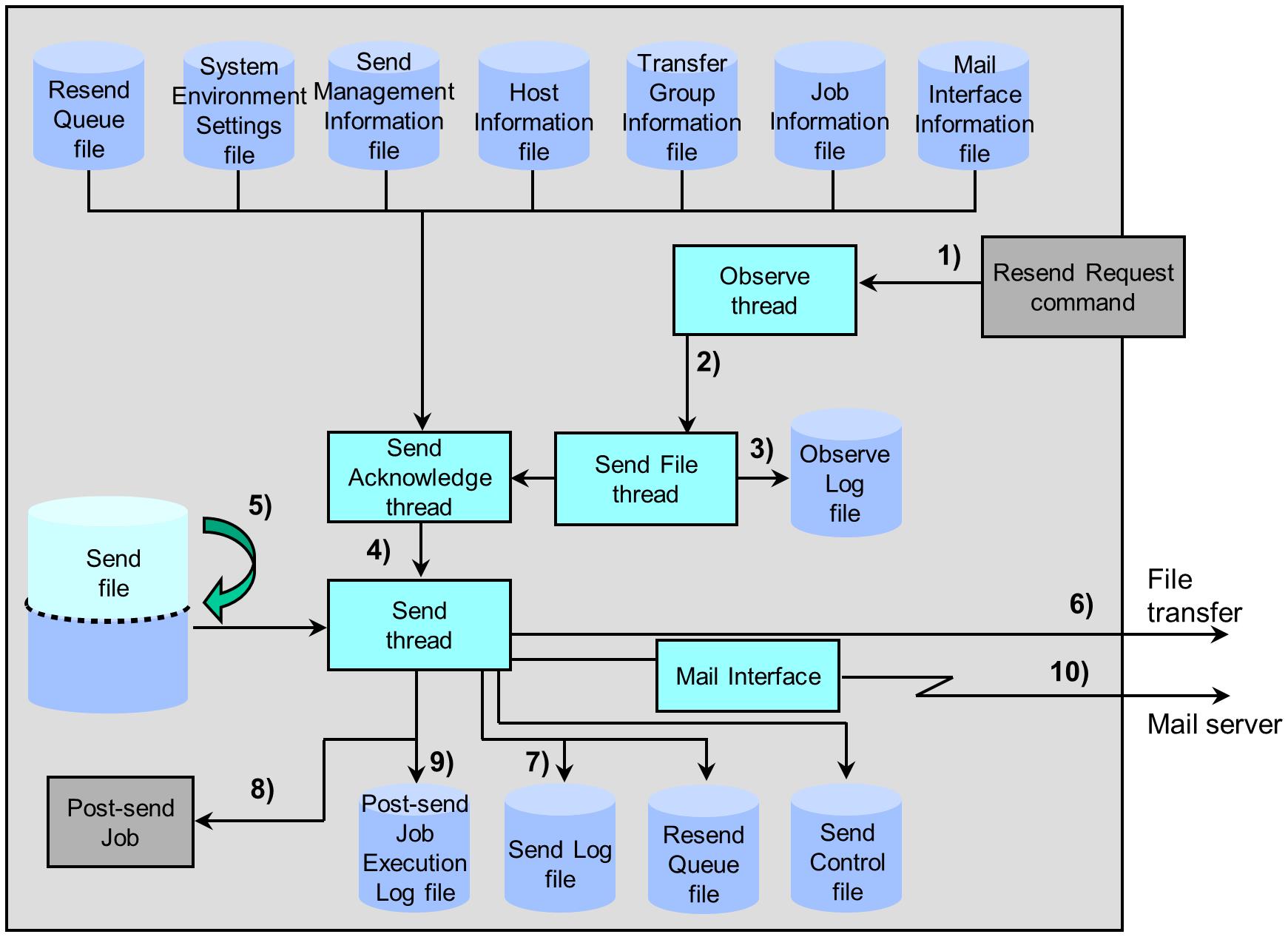
Flow of the Resend Request processing
Resending can also be carried out when you issue the Resend Request command (utlrecv.exe) as a request from the receiving side. This is called the 'Resend Request' in HULFT. When you issue the Resend Request, the Send system carries out the transfer from the point where the Send processing was interrupted (checkpoint). This transferring is called the 'Checkpoint Resend Request.' This function is useful for Send files with a large data volume, because the data that has already been sent is not transferred again. If you issue the Resend Request without specifying the Checkpoint Resend Request, the data is transferred from the beginning. Use this option if it is necessary to transfer data from the beginning, such as when changes are made in the Send file after an unsuccessful transfer.
This processing is based on the assumption that both the Send process and the Observe process on the sending side and the Receive process on the receiving side have already been started.
The flow of the Checkpoint Resend Request is illustrated in Figure 2.6 .
1) Issuing the Resend Request command
The Observe thread acknowledges the Resend Request from the receiving side. In the case of resending, the Pre-send Job is not started even when it is set in the Send Management Information.
2) Issuing the Resend File command (utlsend.exe)
The Observe thread issues a request for resending to the Send File thread.
3) Writing the request to the Observe Log file
The Send File thread writes the request from the receiving side to the Observe Log file.
4) Creating the Send thread
The Send Acknowledge thread receives the Resend Request and creates a Send thread according to the criteria in the Resend Queue file (sddreqls.dat) and each management information file.
5) Skipping reading of the Send file
The Send thread determines the sent size and the sent record count from the Resend Queue file and skips the reading of data that has already been transferred.
6) Carrying out Send processing
The Send thread carries out Code Conversion and file compression based on the settings of the transferred Send Management Information, then transfers the unsent data of the Send file to the remote host. Data is transferred from the beginning of the Send file when the Checkpoint Resend Request is not specified when the host on the receiving side issues the Resend Request.
7) Writing the result to the Send Log file
The Send thread writes the result of the Send processing in the Send Log file after the processing is complete.
In addition, if the Send processing ends unsuccessfully, the Send thread writes the information about the failed transfer into the Resend Queue file (sddreqls.dat).
8) Starting up the Post-send Job
The Send thread activates the Post-send Job that is registered in the Job Information according to the condition that is registered in the Send Management Information. HULFT activates either the job that is specified for the successful end of the sending or the one for the unsuccessful end of the sending, depending on the transfer result.
9) Writing the result to the Post-send Job Execution Log file
The Send thread writes the job execution results to the Post-send Job Execution Log file.
10) Triggering an email
The Send thread triggers to send an email according to the settings that are registered in the Mail Interface Information.
When HULFT carries out the Send File or Send Request, any queue records with the same criteria as the Send processing are deleted from the Resend Queue. To specify the criteria for the deletion, set Criteria to Delete Resend Queue (resenddel) in the System Environment Settings.