Outline of operation logs
Operation logs are output when a request is issued to HULFT, when a command of HULFT is executed, or when HULFT accesses a system file.
The operation logs output by the Send processing and the Receive processing are shown below:
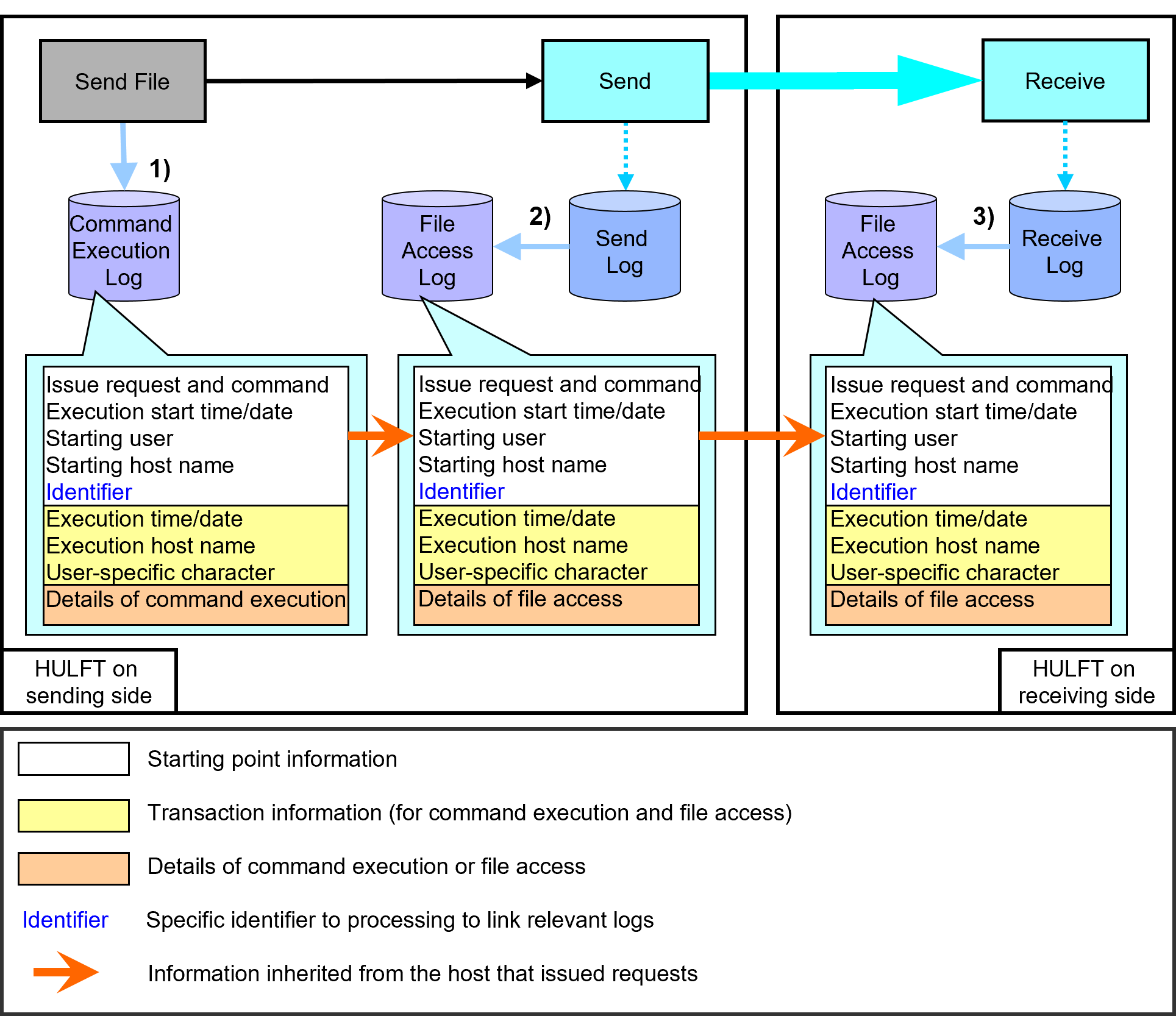
Figure 2.38 Operation Logs in Send Processing and Receive Processing
1) When the Send File is issued on the HULFT Management Console or in the command line, the date/time of issuing the request, the user ID, the host name, and the like are output to the Command Execution Log file of HULFT on the sending side.
2) When the Send process is executed based on the Send File and a Send Log is added, the date when the log was added, the information that identifies the added log, and the like are output to the File Access Log file of HULFT on the sending side.
3) When the Receive process is executed and a Receive Log is added, the date when the log was added, the information that identifies the added log, and the like are output to the File Access Log file of HULFT on the receiving side.
File Access Log and Command Execution Log
The records of file access and the records of request issuance or command execution are output to separate logs files (the File Access Log file and the Command Execution Log file, respectively).
|
Variety of Operation Log |
Output Destination |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
File Access Log |
HULPATH/ |
The Log is output when information is added, updated, or deleted in system files, such as System Environment Settings, system management information, various logs, and the like. |
|
Command Execution Log |
HULPATH/ |
The Log is output when a request is issued or a command is executed. |
Refer to Format and reference keys in operation logs for target system files, target types of file access, and issue requests or commands of operation logs.
-
The File Access Log is output when the contents in the system file are modified. Merely referencing a file without modifying it does not output the Log.
-
The Command Execution Log is output by the host on the side where a request or command was executed. The Observe Log as well as the File Access Log that carries the record of the addition in the Observe Log are output by the requestee-side host.
-
Where multiple records are deleted from system management information or logs by specifying the target range, the Command Execution Log outputs only one entry, while the File Access Log outputs one entry per deleted record.
-
Records of the internal operations of the system are not output to the operation logs, because the purpose of the logs is to keep records of operations performed by users.
Information output to the operation log
Information output to the operation log is divided roughly into the following categories: information on request issuance or command execution that is an origin of a series of transactions (starting point information), information on the transaction performed according to request issuance or command execution (transaction information), information specific to the File Access Log, and information specific to the Command Execution Log.
The following information is output to the operation log in CSV format:
Starting point information
Starting point information is the starting information when a request is issued or a command is executed. Notification of the information is sent to the connection destination, and the same information is used by all the File Access Logs and the Command Execution Logs within one transaction.
Notification of fields other than user ID in the starting point information is always sent to the connection destination when the operation log output function is used.
- Execution Start Time/Execution Start Date
-
Time and date when request issuance or command execution started
This date and time are set in the operating system of the starting host.
- User ID (OS) and User ID (Management Console)
-
User IDs of the user who performed the operation
These are the user ID of the operating system on the starting host, and the user ID on the Management Console that issued the request.
Their definitions vary depending on the type of starting host.
Table 2.13 Difference between Definition of User ID (OS) and User ID (Management Console) by Host Type
Host Type
User ID (OS)
User ID (Management Console)
HULFT for Mainframe
User ID of OS
User ID of the user who used the HULFT Management Console
HULFT for Linux/AIX
User Name of OS
Same as User ID (OS)
(When the Management Console Security is disabled, indicated as "")HULFT for Windows
User Name of OS
User Name registered on the Management Console Security
(When the Password Check is disabled, indicated as "")HULFT for IBMi
User ID of OS
Same as User ID (OS)
(When the Management Console Security is disabled, indicated as "")HULFT Manager
User Name of OS
User ID (Management Console) of HULFT at the connection destination
HULFT-HUB Server
User Name of OS
Always indicated as "", because there is no Management Console
HULFT-HUB Manager
User Name of OS
The User Name that logged on HULFT-HUB Server
NoteWhen a user ID (OS) in the operation log contains a multi-byte code, the user ID (OS) appears correctly only if both of the following conditions are met:
-
Both the host type of the starting host and the host type of the connection destination are Windows
-
The system locale is the same for the starting host and the connection destination
If both conditions are not met, the user ID (OS) will not be displayed correctly.
-
- Starting Host Name
-
Name of the local host that performed the operation
Refer to Handling of local host name for details on local host names.
- Identifier
-
Identifier of transaction
A different identifier is generated for each transaction. There are two types of identifier: 'Latest Identifier' and 'Starting Identifier.' Refer to Identifier for the Latest Identifier and the Starting Identifier.
Identifiers can link the record that is output to the operation log file with the record in the log (Send Log, Receive Log, or Observe Log), because the identifiers are also output to the log (Send Log, Receive Log, or Observe Log).
Transaction information
Transaction information is the information at the time when a file is accessed, or request issuance or command execution is processed.
- Execution Time/Execution Date
-
Time and date when file access, or request issuance or command execution was processed
This is the time and date set in the OS of the execution host.
- Execution Host Name
-
Local host name of the host on which file access, or request issuance or command execution was processed
Refer to Handling of local host name for details on local host names.
- Operation Log User-specified Character
-
Character string to identify HULFT that outputs the operation log
Operation Log User-specified Character (oplcharacter) is a character string to identify which HULFT environment outputs which operation log, when the operation logs output by two or more HULFT environments are accumulated.
Table 2.14 Values Set to Operation Log User-specified Character
Host Type
Values Set to Operation Log User-specified Character
HULFT for Mainframe
Operation Log User-specified Character (OPLCHARACTER) in the System Environment Settings
HULFT for Linux/AIX
HULFT Identifier (hulcharacter) in the System Environment Settings
HULFT for Windows
Operation Log User-specified Character (oplcharacter) in the System Environment Settings
HULFT for IBMi
HULFT Identifier (hulcharacter) in the System Environment Settings
HULFT Manager
Operation Log User-specified Character in the System Environment Settings
HULFT-HUB Server
Service Name (ServiceName) in the System Environment Settings
HULFT-HUB Manager
User-specified Character in the System Environment Settings
Specific information to the File Access Log
Specific information to the File Access Log is the information on the types and targets of file access. It is output only to the File Access Log file.
Refer to Format and reference keys in operation logs for the list of the output values.
- File Access Type
-
Types of file access
File Access Type refers to varieties of operation, such as addition, modification, or deletion.
- System File Type
-
System file that is a target of file access
This is an identifier that indicates the system file targeted for file access.
- File Key Information
-
Fields in the file that are targets of file access
File Key Information is additional information to identify the record that was accessed when two or more records are stored in one file, such as in the system management information files or log files (Send Log, Receive Log, or Observe Log).
Specific information to the Command Execution Log
Specific information to the Command Execution Log is information regarding the processed requests and commands. The information is output only to the Command Execution Log file.
Refer to Format and reference keys in operation logs for the list of the output values.
- Command Execution Key
-
Type of request issuance or command execution
This identifier indicates the processed request issuance or command execution.
- Command Issued by
-
Issuer of requests or commands
This identifier indicates the source of requests or commands, such as whether the command was executed in a command line, and whether the request was issued on the HULFT Management Console.
- Command Parameter
-
Parameter of the command
Command Parameter is a parameter specified when the parameter command is executed.