Connection between Networks
When you connect servers between networks, you must connect two Neighboring Servers (connection line settings) and then configure the settings that are related to routing (Routing Information settings). Connecting two Neighboring Servers is called 'connection between servers.'
Connection between Two Controlled Servers
When you connect two controlled servers, you must log in as a user with the following conditions:
- The user can log in to both servers that you connect (that is, the user has been registered to both servers).
- The user has the Permission to Connect Servers for both servers that you want to connect.
- The user has the Permission to Configure System Environment Settings for which 'Allow to Update' is specified for both servers that you connect.
The procedure for connecting the servers is as follows:
-
Click the [Connection Line] on the [Insert] menu.
The Structure Diagram enters connection line edit mode (the icon of the [Connection Line] on the [Insert] menu is highlighted and
 on the toolbar is in a pressed state).
on the toolbar is in a pressed state). -
On the Structure Diagram, press and hold the left mouse button on one server icon and drag the mouse cursor to another server icon.
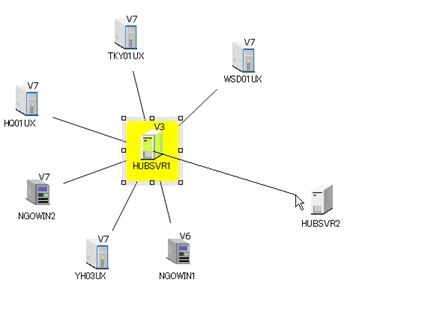
-
When you release the left mouse button, a connection line is drawn and the Registered Clients of the connection destination server are added to both the Structure Diagram and the Structure List.
If the password is different between the connection destination server and the login server, a login dialog box appears. Enter the password for the connection destination server.
[Note] You cannot change the user ID. 
[Remarks] After the connection line is configured between the servers, the connection line edit mode is automatically cancelled (  on the toolbar returns to a non-pressed state).
on the toolbar returns to a non-pressed state).[Note] - If the message 'A host with the same host name and service name exists. Delete the Host Name: xxxxxxxxxx, modify the service name, and register again.' appears, a client has been registered to both servers that you tried to connect. Remove the client from one of the servers and then connect between the servers again. - When you configure a connection line to connect between servers, check beforehand that each HULFT-HUB Server that you connect is operating. If HULFT-HUB Server is not operating, the information of the Neighboring Server cannot be registered correctly and transfers via the Neighboring Server do not end successfully. If the Neighboring Server that you connect is a server outside of control, the information of the Neighboring Server is registered correctly, even if it is not operating. -
Double-click one of the servers on the Structure Diagram and click the [Neighbor Server]. The Neighboring Server Information appears.
On this screen, specify whether the login server monitors the operation of the connection destination server.
[Remarks] - Specify in the System Environment Settings of the connection destination server whether or not the connection destination server monitors the operation of the login server. - For details on the Neighboring Server Information, refer to Neighboring Server Information in Management Information Reference. 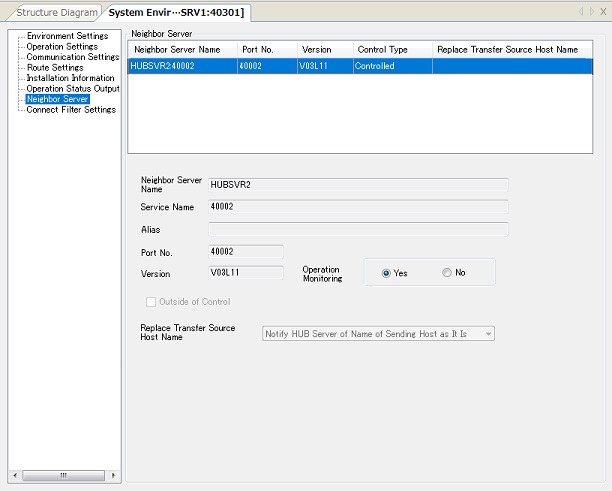
- Click the Route Settings option. The Server Routing Information appears.
-
Enter the network address and other information of a Neighboring Server in the Server Routing Information, and then click the [Add] to register the routing information to the list (marked as 1, 2, and 3 on the screen below).
Check that all Neighboring Servers have been registered correctly.
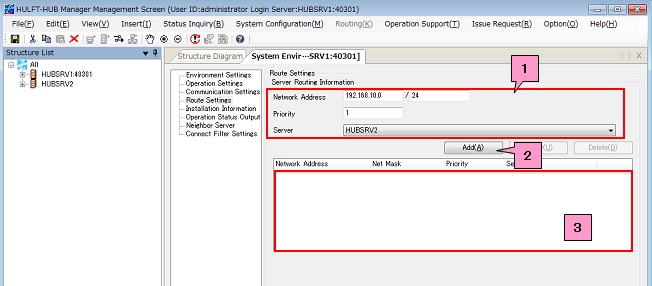
<Table> Server Routing Information
Field Name Description Type Restriction Specification Network Address This field specifies the network address of the destination network in the format of 'network address/net mask.'
Example: Case where the IP address is 192.168.10.100 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0
Network address is 192.168.10.0/24
Network Address/Net Mask Network address: from 0 to 255
Net mask: from 1 to 32
Mandatory Priority This field specifies the priority for routing. Numeric value From 1 to 256 *1 Mandatory Server This field specifies the server that is used to connect to the destination network. - All servers that are registered on the Structure Diagram Mandatory *1: The smaller the numeric value, the higher the priority it is given.
-
Specify a default server as needed.
<Table> Default Server
Field Name Description Type Restriction Specification Default Server This field specifies the server that is used as a transfer destination if the specified route cannot be found. - All servers that are registered on the Structure Diagram Optional - After you configure all settings, click
 on the toolbar.
on the toolbar.
When Unable to Log In to Connected Server
If you are unable to use the user ID and password for the login server to log in to a connected server, the following screen appears after step 2.
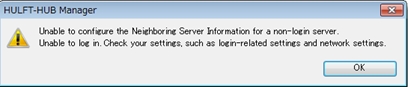
If you click the [OK], the target server is registered as a 'not operating' server (gray icon).
You cannot view the management information or log records for 'not operating' servers.
The following types of problems may have occurred on the target server:
- Daemon has not been started up
- The setting for the user ID or the password is incorrect
Resolve the problem and perform the Reconnect procedure to reset the server as a controlled server.
| [Note] | If the ID that is registered to the connection destination server is the same as the login server but the password is different between these servers, a dialog box for logging in to the Neighboring Server appears. If you enter the correct password on the login dialog box, HULFT-HUB Manager registers the server as a controlled server. If you click the [Cancel], HULFT-HUB Manager registers the server as a 'not operating' server. |
| [Remarks] | On the Management screen, a dashed line is displayed for a connection line that represents a connection to a 'not operating' server. |
| The icon for a server to which you cannot log in appears in gray, even after the server is connected by a connection line. |
Connection between Controlled Server and Server outside of Control
When you connect a controlled server and a server outside of control, you must log in as a user with the following conditions:
- The user can log in to the controlled server that you connect (that is, the user has been registered on the server).
- The user has the Permission to Connect Servers for the controlled server.
- The user has the Permission to Configure System Environment Settings for which 'Allow to Update' is specified for the controlled server.
The procedure for connecting a controlled server and a server outside of control is the same as the procedure for connecting two controlled servers.
Contact the administrator of the server outside of control to check the settings of the server outside of control.