TO_INCODE function
Function
TO_INCODE{KANJI[,STRING_TYPE[,EBCDIC]]}
This function converts the target character string to the input character encoding by using the specified method.
External characters and user code tables cannot be used. All characters in Shift JIS, IBM kanji, UTF-8, and UTF-16 can be converted.
For the DataMagic Desktop grade, the TO_INCODE function cannot be used. An execution error occurs if this function is used.
Parameters
KANJI
Specify the Kanji code type that applies to the character string to be converted.
The table below describes the setting values for kanji encoding types.
|
Setting value |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
S SJIS |
Convert from Shift JIS to the input-character encoding. |
|
E EUC |
Convert from EUC to the input-character encoding. |
|
8 UTF-8 |
Convert from UTF-8 to the input-character encoding. |
|
6 UTF-16 |
Convert from the Unicode byte order of the UTF-16 local host kanji encoding type to the input-character encoding. (Windows, Linux: Little Endian) (UNIX, zLinux: Big Endian) |
|
UTF-16BE |
Convert from UTF-16 Big Endian to the input character encoding. |
|
UTF-16LE |
Convert from UTF-16 Little Endian to the input character encoding. |
|
I IBM |
Convert from IBM kanji to the input character encoding. |
|
K KEIS |
Convert from KEIS to the input character encoding. |
|
J JEF |
Convert from JEF to the input character encoding. |
|
N NEC |
Convert from NEC kanji to the input character encoding. |
|
Z JIS |
Convert from JIS to the input character encoding. |
|
Other than the above |
Error |
Specification of the same kanji code type for KANJI and for input is acceptable. An error will not occur.
STRING_TYPE
Specify to which type to convert the strings to. (This parameter can be omitted.)
If you omit this parameter, M is set. Null is not regarded as an omission and causes an error.
The table below describes field types of setting values and their descriptions.
|
Setting value |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
X |
Convert as characters. |
|
M |
Convert as variable-length characters. |
|
N |
Convert as double-byte graphic characters. |
|
Other than the above |
Error |
EBCDIC
Specify a single-byte encoding type for target strings. (This parameter can be omitted.)
If omitted, the following values are set.
-
If EUC, Shift JIS, UTF-8, or UTF-16 is specified for Kanji code type, ASCII is set.
-
If IBM, KEIS, JEF, NEC, or JIS is specified for Kanji code type, EBCDIC KANA is set.
If EUC, Shift JIS, UTF-8, or UTF-16 is specified for the kanji encoding type, you can set ASCII only. Even if you specify other encodings, the conversion is processed as ASCII.
ASCII can specify EUC, Shift JIS, UTF-8, UTF-16, and JIS only. An error occurs if a different kanji encoding type is specified.
|
Setting value |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
A EBCDIC KANA |
Convert by EBCDIC kana. |
|
B EBCDIC LOWERCASE |
Convert by EBCDIC lowercase. |
|
C EBCDIC ASCII |
Convert by EBCDIC ASCII. |
|
D EBCDIC ASPEN |
Convert by EBCDIC ASPEN. |
|
E IBM STANDARD |
Convert by Japan (Latin) for IBM. |
|
F IBM STANDARD EXTENSION |
Convert by Japan (Latin) Extended for IBM. |
|
G NEC KANA |
Convert by NEC Katakana. |
|
H IBM KANA EXTENSION |
Convert by Japan (Katakana) Extended for IBM. |
|
Z ASCII |
Convert by ASCII. |
|
Other than the above |
Error |
Input/output relationships
The table below explains the relationships between the field type of input data and the field type of output data.
|
Input |
Output |
|---|---|
|
X |
Type specified by the conversion method |
|
N |
Type specified by the conversion method |
|
M |
Type specified by the conversion method |
|
D |
Error |
|
CSV character string |
M |
|
W |
Error |
|
9 (numeric character string) |
9 (numeric character string) (unconverted) |
|
I |
Type specified by the conversion method |
Example
Assuming that you have input files for which the character encoding is UTF-8, and they include CSV input data for which the first field is in Shift JIS encoding and remaining fields are in UTF-8 encoding, you can use the TO_INCODE function to convert the encoding of the first field to UTF-8.
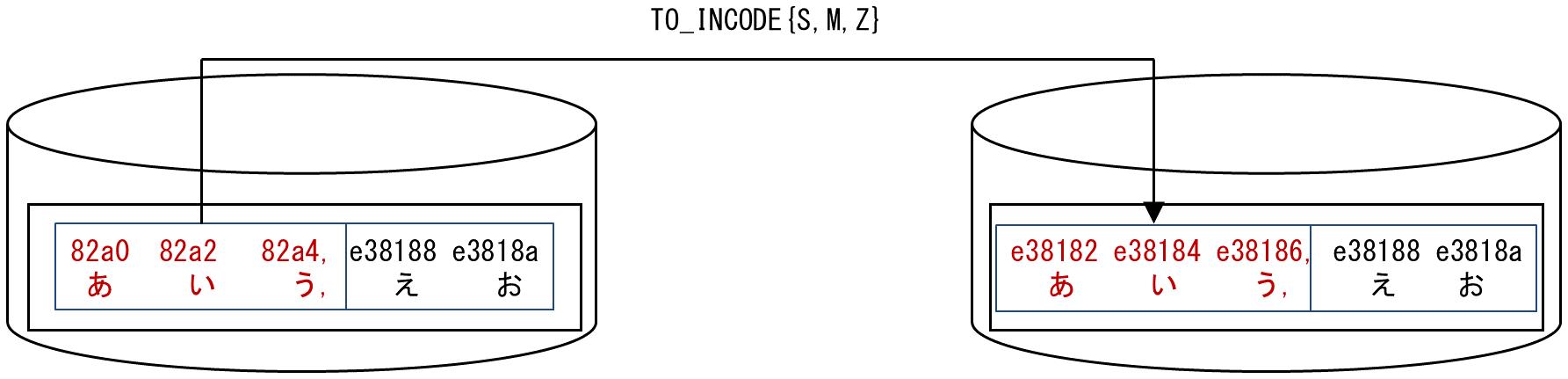
Figure A.53 Example of using the TO_INCODE function