Components that can be used in common components
A component is a processing unit of data processing execution. You can select a component type and then create common component information. Creating common component information allows you to execute the operation that corresponds to the specified common component ID in output settings, extraction conditions, and post processing.
|
Component name |
Processing |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
Date |
Converts to the date of the start time of data processing. Whenever this component is called, this component returns the character string based on the same date. |
Used to standardize the particular date format and to unify output. |
|
Time |
Converts to the time of the start time of data processing. During the period until data processing finishes, a character string is returned based on the same time. |
Used to standardize the particular time format and to unify output. |
|
Fixed character string |
Returns a fixed character string. |
Used to unify the output of the particular character string and also simplify changes. |
|
Fixed numeric character string |
Returns a fixed numeric character string. |
Used to unify the output of the particular numeric character string and simplify changes. |
|
Function |
If a function is used in the first layer, the function is executed to the mapped field and then the function returns a value. If mapping is not performed by using necessary functions in the first layer, an error will occur. In the second layer onwards, the returned value of the previous component overwrites the argument specified as the returned character string of the previous component. The argument of the previous component is inherited as the arguments other than the above. |
Used for the purpose of standardizing the operations used across multiple functions. |
|
Virtual query |
Executes the same operation as executing queries to virtual tables. Five arguments (ARG1 to ARG5) can be used. Virtual tables cannot be used. |
Provides processing that cannot be performed only through functions such as select case, numeric operation, and date operation. |
|
In a virtual query for initial processing, you can specify any number of SQL statements (DDL and DML) by delimiting them with semicolons (;). SQL statements are executed in the order in which they are written. If multiple SQL statements are specified, the value of the last statement is used as the return value. |
Creates a virtual table and data during the initial processing component and uses them within an ordinary component. |
|
|
Lua scripts |
Executes conversion processing by using a Lua script. |
Used to create customized processing. |
In addition, templates whose name have the prefix "SAISON_" are provided for common components.
Because the templates with the prefix "SAISON_" may be updated in future, copy and rename the templates before editing and using them.
|
Common component ID |
Description of processing |
|---|---|
|
SAISON_BEFORE_DATE |
Returns TRUE if the input date is earlier than the execution date for data processing, and returns FALSE if that is not the case. |
|
SAISON_CHECKLEN |
Checks whether the input string length is within the specified number. Returns an empty string for normal, and an error message for exceed. Multibyte characters and variant characters are also counted as one character.
The output error message is as follows: [Error Message] The maximum number of characters for item ("Argument2") is "Argument1", but "Number of characters in input data" characters have been entered: Input data ("Input data")
*The red text will be replaced with the corresponding data and output. |
|
SAISON_DATE_CHECK |
Returns TRUE if the input character string is in the date format YYYY/MM/DD, and returns FALSE if that is not the case. |
|
SAISON_FORMAT_DATE_OR_NULL |
Converts the target character string based on the specified date format. If the character string is null or only blank characters(including tabs and line breaks), null is returned. |
|
SAISON_M10W21 |
Calculates check digits using modulus 10 with 2:1 weighting. |
|
SAISON_MTOI |
Converts a hex string to a binary value. If "0X" or "0x" exists at the beginning, it is ignored and only the subsequent hex string is converted. If another prefix or value consisting of other than hex characters is input, operation is not guaranteed. |
|
SAISON_PACK2NUMSTR |
Converts a signed internal decimal number into a numeric character string. If the value in the digit portions or sign portion is invalid, null is returned. |
|
SAISON_PAD |
The specified character string is repeatedly padded until it reaches the specified size. |
|
SAISON_REPLACE_HEX |
If the hexadecimal character string specified in argument 1 exists in an input character string, the string is replaced with the hexadecimal character string specified in argument 2. |
|
SAISON_REPLACE_REG |
This is an extended version of REPLACE_REG. The replace string can be specified as a hexadecimal string (\xHH) in UTF-8 format. |
|
SAISON_STRLEN |
Gets the number of characters in the input string. Multibyte characters are counted as one character. Variant characters are also counted as one character. |
|
SAISON_SUBSTR |
Obtains a string with a specified number of characters from an input character string starting from a specified position. |
|
SAISON_TOLOWER |
Converts uppercase characters of the input character string to lowercase. |
|
SAISON_TOUPPER |
Converts lowercase characters of the input character string to uppercase. |
(1) Using SAISON_CHECKLEN
SAISON_CHECKLEN can be used to detect when the number of characters in a character string exceeds the limit. However, the procedure to then have the data processing end in an error is somewhat complicated. An example of application is shown below.
In the below example, it is detected that the number of characters entered exceeds the limit, a detailed message is displayed, and the processing ends in an error.
1. Create a variable to receive the return value of SAISON_CHECKLEN
Create the variable to which the error message that is received as the second argument of SAISON_CHECKLEN is assigned. (In this example, the variable name is "ERR_COUNTOVER".)
As SAISON_CHECKLEN is designed to return null if the check result is normal, assigning one variable for the return value is sufficient even if there are multiple character strings to be checked (depending on how you intend to use this function, you can also choose to prepare multiple variables).
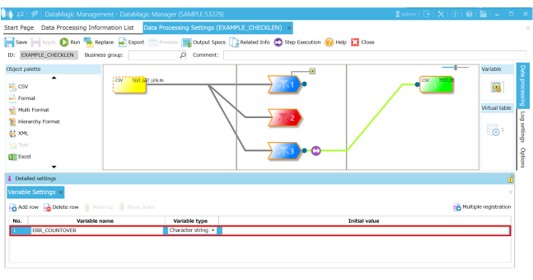
Screen 5.7 The Data Processing Settings screen (example of creating variables)
2. In Variable Assignment Settings, assign the results of the check whether the character limit has been exceeded to the ERR_COUNTOVER variable
On the Data Processing Settings screen, double-click the Variable assignment icon.
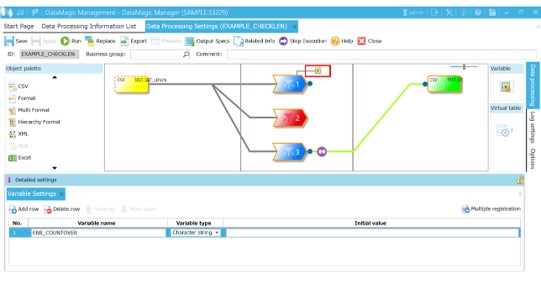
Screen 5.8 The Data Processing Settings screen (double-clicking the Variable assignment icon)
The Variable Assignment Settings screen appears.
In this example, the check is performed on multiple fields and the result is assigned to a single variable, ERR_COUNTOVER.
If an error occurs in multiple fields, all the error messages are concatenated and assigned to the ERR_COUNTOVER variable.
As it is possible there is already a value assigned to the variable ERR_COUNTOVER, ensure that if further values are to be assigned, the character string will be concatenated to the existing variable.
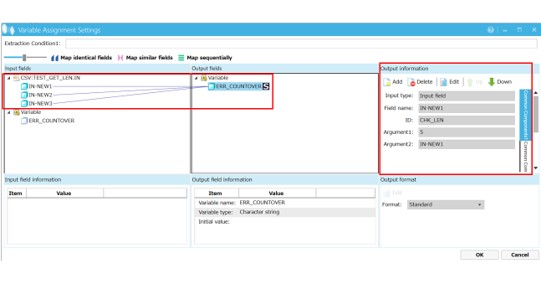
Screen 5.9 Variable Assignment Settings screen
3. Using Custom Error Condition, configure settings so that if the ERR_COUNTOVER variable is not null, the processing ends in an error
In this example, if it is detected that the number of characters exceeds the limit and an error occurs, the error message is assigned to the ERR_COUNTOVER variable.
The content of the error message are output as the detailed message, and the processing ends in an error.
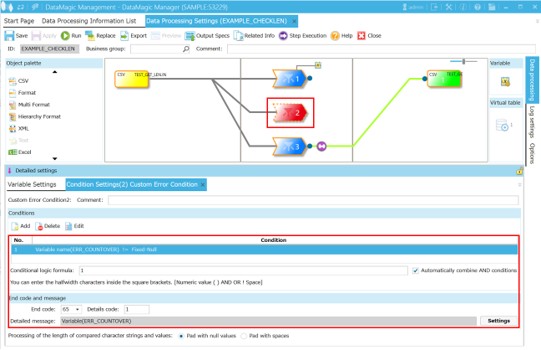
Screen 5.10 Data Processing Settings screen (setting custom error conditions)