Digits after the decimal point
In the Format Information and Data Processing Settings (Mapping Information), Digits after Decimal Point refers to the digits after a decimal point when that data is converted into a decimal number.
(1) Digits after the decimal point of the input data
Set the number of bytes to be regarded as the decimal part of the input data when it is converted into a decimal number. The following is an example.
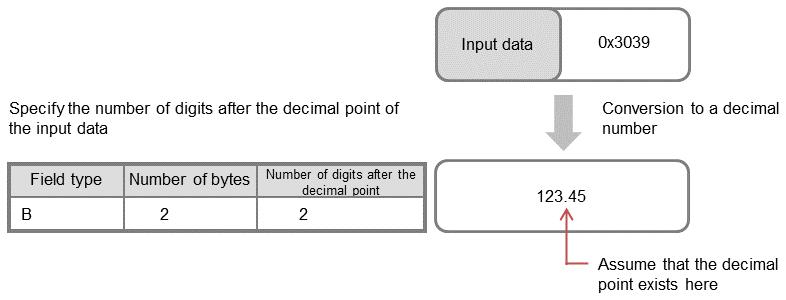
Figure 4.108 Digits after the decimal point of the input data
In this example, a 2-byte B data type is converted into the decimal "12345", and based on the setting of digits after the decimal point = 2, the 2 lowest bytes are regarded as the decimal part, and therefore the data is finally converted into "123.45".
(2) Digits after the decimal point of the output data
For the output data, set the number of bytes that are output in the decimal part. The following is an example.
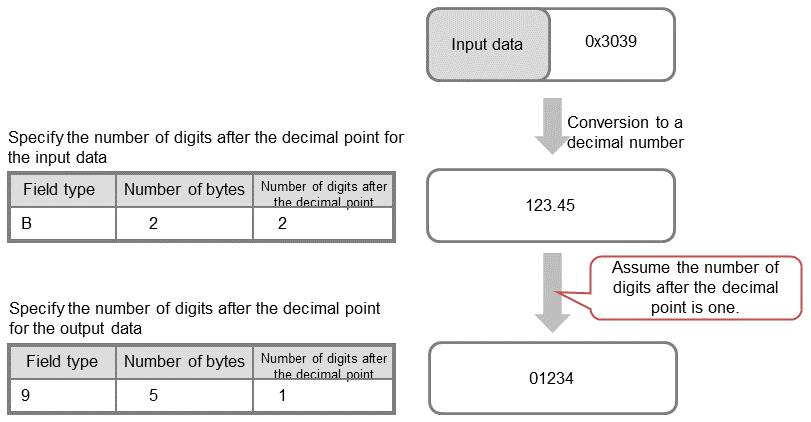
Figure 4.109 Digits after the decimal point of the output data
In this example, as in the example of the input data, a 2-byte B data type is converted into "123.45". Then, because Digits after Decimal Point is set to 1 for the output data, the number of digits after the decimal point is 1, and the resulting output data is determined to be "123.4". Because the output setting is 5-byte type 9, to meet the required number of bytes, a zero (0) is padded at the beginning and the data is finally converted to "01234" (because numeric data items do not contain decimal points).
(3) Conversion examples
a) Digits after the decimal point for conversions between field types
The table below shows examples of relationships between the bytes and the digits after a decimal point for conversions between field types.
|
Input data |
Output data |
Input data |
Output data |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
No. of bytes |
Digits after decimal point |
No. of bytes |
Digits after decimal point |
Internal representation |
Value |
Internal representation |
Value |
|
5 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
12345 |
12345 |
0012345 |
0012345 |
|
5 |
2 |
7 |
0 |
12345 |
123.45 |
0000123 |
0000123 |
|
5 |
2 |
7 |
1 |
12345 |
123.45 |
0001234 |
000123.4 |
|
5 |
2 |
7 |
2 |
12345 |
123.45 |
0012345 |
00123.45 |
|
5 |
2 |
7 |
4 |
12345 |
123.45 |
1234500 |
123.4500 |
|
5 |
2 |
7 |
5 |
12345 |
123.45 |
2345000 |
23.45000 |
|
5 |
2 |
7 |
7 |
12345 |
123.45 |
4500000 |
0.450000 |
b) Digits after a decimal point for conversion from field types to CSV or XML types
The table below shows examples of relationships between the bytes and the digits after a decimal point for conversion from field types to CSV or XML numeric values.
|
Input data format |
Input data |
CSV or XML format data |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Field type |
No. of bytes |
Digits after decimal point |
Internal representation |
Value |
|
9 |
5 |
2 |
0x3132333435 |
123.45 |
|
P |
5 |
2 |
0x000012345D |
-123.45 |
|
S |
5 |
2 |
0x3132333455 |
-123.45 |
|
B |
4 |
2 |
0x00003039 |
123.45 |
In the above table, "d" is used to represent the internal minus sign, "3" the zone sign, and "5" the external minus sign.
c) Digits after a decimal point for conversion from CSV or XML to field types
The table below shows examples of relationships between the bytes and the digits after a decimal point for conversion from CSV or XML numeric values to field types.
|
Input data |
Output data format |
Output data |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CSV or XML |
Digits |
Digits after decimal point |
Field type |
Internal representation |
Value |
|
123.45 |
5 |
0 |
9 |
00123 |
00123 |
|
123.45 |
5 |
2 |
9 |
12345 |
123.45 |
|
123.45 |
5 |
4 |
9 |
34500 |
3.4500 |
|
123.45 |
7 |
2 |
9 |
0012345 |
00123.45 |
|
123.45 |
7 |
4 |
9 |
1234500 |
123.4500 |
|
123.45 |
7 |
7 |
9 |
4500000 |
0.4500000 |